
A set of attribute that describes the real world (e.g., employees) with attributes (e.g., employee_id)
Entity set: A collection of similar entities
Each entity set has a key
Each attribute has a domain (type)
Relationship: An idea of a relationship
Think of the relationship when creating views.
Constraints#
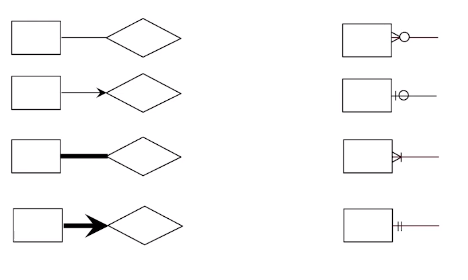
Key constraint:
One to Many: A key constraint on an entity such that each row of the entity can point to many rows of the other entity.
Many to Many: If there are no key constraint on an entity such that any row of the entity can point to any row of the other entity.
One to one: If there are key constraint on both entity then each row of each entity can only point to one.
One to many and one to one implies at most one
Participation constraint:
A participation constraint on an entity such that every row must be part of the relationship to another entity.
This implies at least one.
Weak Entities#
An entity owned by a primary key of the another (owner) entity that isn’t a full entity.
Must have total participation.
A weak entity has a partial key which can be a full key once it relates to its owner entity’s primary key.
Entity to Schema#
Key Constraints
One to One:
FK(pk_1), FK(pk_2)
Participation Constraint
Full participation =
NOT NULL
Weak entity
Composite key on id and the foreign key
PK(pk, fk), FK(fk)