Introduction#
Text search is done with a search engine (aka informational retrieval system).
Document : A file, website, or generally a collection of unstructured data that can be text searched.
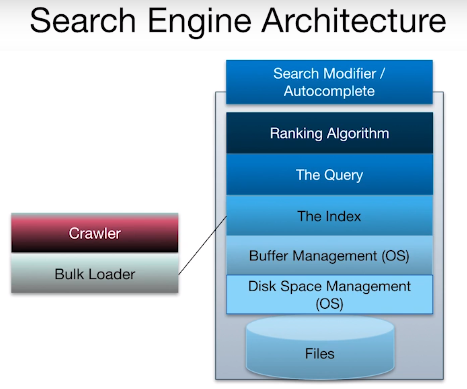
Architecture#
Informational retrieval system (IR) are structured similar to a DBMS however differs in such ways:
No relational operations
Ranks top result with no need to finish finding all that satisfy the query
A crawler used to import data as it updates
Bag of Words Model#
The bag of words model treats a document collection of searchable terms by its words. The bag of words model would implement the following methods:
Ignore Stop Words: Filter useless non-informative words.
Common english articles (e.g., the, a, an)
HTML tags
Stemming: Converting word to its basic form.
Tenses to base/present tense (e.g.,
walked -> walk).
Boolean Text Search#
A simple search algorithm that made up of simple boolean statements.
For example, find a document with “California” and “school”.
Postings List#
For each documents, its words will be extracted and placed into the file system as a postings list. A postings list is a schema of (text term, text docID). We will call this “table” the InvertedFile
Search Index#
The search engine will have a search index of the InvertedFile ordered by docID.
Important: From here on, queries we made must use a single table per keyword.
Positional data: We may add the position of the term that would benefit nearby word search.
Boolean Text Search#
A simple text operation using boolean that slices the document to match the boolean query.
For example this query is equivalent of an intersection between the three keywords Berkeley, Database, Research,
SELECT IB.docID
FROM InvertedFile IB, InvertedFile ID, InvertedFile IR
WHERE IB.term = "Berkeley"
AND ID.term = "Database"
AND IR.term = "Research"
AND IB.docID = ID.docID AND ID.docID = IR.docID